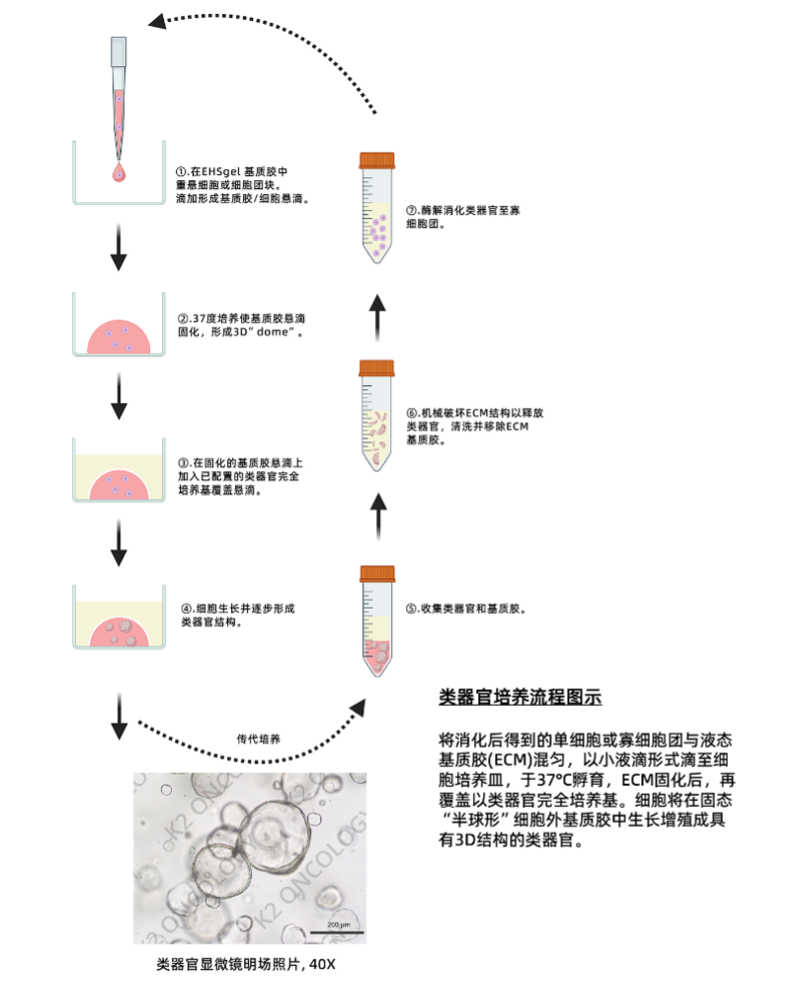
-
胰腺癌类器官培养试剂盒
KPC-100
-

胰腺癌类器官培养试剂盒
KPC-1000

OrganoPro™胰腺癌类器官培养基套装
KPC-100 包含以下产品
- OrganoPro™胰腺癌培养基 100mL
- OrganoPro™胰腺癌添加剂成分A 2mL
- OrganoPro™胰腺癌添加剂成分B 1mL
KPC-1000 包含以下产品
- OrganoPro™胰腺癌培养基 1000mL
- OrganoPro™胰腺癌添加剂成分A 10mL x 2
- OrganoPro™胰腺癌添加剂成分B 10mL
科途医学 科学家

名字
PhD
我们的科学家向您推荐
我们的产品简化了实验流程,集成多种因子,无需单独优化,扩增潜力高,14天内细胞数量可达到1×10^6。适用于多种培养形式,包括基质胶、低吸附孔板和生物反应器悬浮培养。GMP级别生产条件下制备,批次质量稳定,试剂含量是常规市售干细胞培养基的2倍,实现极佳的成本效益比。让复杂的培养变得简单快速,让科研变得更高效。
概览
此产品基于 Simumatrix 技术平台,通过工业化高通量筛选,针对中国高发的肿瘤类型进行培养基优化筛选而开发出的类器官培养基产品,可用于胰腺癌的类器官培养。
产品优势/特点:
- 简单易用,节省验证时间:提供详细操作方案,产品使用简便,节省研究者大量类器官培养摸索验证时间;
- 肿瘤组织覆盖类型广:覆盖多达15个组织瘤种,>900种肿瘤驱动基因突变模型;
- 扩增潜力高:自研高活力高稳定性WNT与RSPOs,支持肿瘤类器官多代次连续稳定培养;
- 肿瘤类器官验证数据齐备:多维类器官验证数据的整合,类器官驱动基因突变及表达谱,类器官组织病理学验证及类器官药敏数据等。
- 多篇高分文献应用:多篇高分文献应用,口碑卓越;
- 自主研发,产能充足,性价比高:全自研生产,源头品控,产品性价比高。
产品组成:
| 产品名称 | 货号 | 规格 | 储存温度 | 保质期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OrganoPro™ Pancreatic Cancer Organoid Culture Medium 人源胰腺癌类器官培养基 | KPC-100/1000-M | 100mL / 1000mL | 2-8°C | 12个月 |
| OrganoPro™ Pancreatic Cancer Organoid Culture Supplement A(50X) 人源胰腺癌类器官培养基添加剂A(50X) | KPC-100/1000-A | 2mL / 20mL | -20°C | 12个月 |
| OrganoPro™ Pancreatic Cancer Organoid Culture Supplement B(100X) 人源胰腺癌类器官培养基添加剂B(100X) | KPC-100/1000-B | 1mL / 10mL | -20°C | 12个月 |
类型
类器官培养基
适用细胞
胰腺癌类器官
物种
人类
应用
培养人源胰腺癌类器官
商标
OrganoPro™
产品使用说明及支持信息
在产品文档中查找支持信息和使用说明,或在下方探索更多
| 文档类型 | 产品名称 | Catalog # |
|---|---|---|
| User manual | OrganoPro™胰腺癌类器官培养基套装 | KPC-100 KPC-1000 |
资源及文献引用
相关资源及文献引用
Nuclear to Cytoplasmic Transport Is a Druggable Dependency in HDAC7-driven Small Cell Lung Cancer
Tingting Qin, et al. | Advanced Science (2025)
Abstract:
Immunotherapy has gained approval for use in small cell lung cancer (SCLC), yet only a subset of patients (10-20%) experience meaningful benefits, underscoring the urgent need for more effective therapeutic approaches. This work discovers a distinct HDAC7-high SCLC phenotype characterized by enhanced proliferative potential, which recurs across various subtypes and serves as a predictor of poorer survival outcomes. By analyzing public datasets, this work finds a strong correlation between c-Myc and HDAC7. RNA sequencing and cellular experiments show that XPO1 is a key regulator in the HDAC7/c-Myc axis. HDAC7 promotes β-catenin deacetylation, phosphorylation modulation, nuclear translocation, and formation of the β-catenin/TCF/LEF1 complex, which binds to c-Myc and XPO1 promoters. Activation of the HDAC7/β-catenin pathway upregulates c-Myc and XPO1 expression, while c-Myc also boosts XPO1 expression. Given the difficulty in targeting c-Myc directly, this work tests selinexor and vorinostat in SCLC xenograft models, with selinexor showing superior results. High HDAC7 expression is linked to increased SCLC proliferation, poorer prognosis, and enhanced sensitivity to selinexor in SCLC cell lines and organoid models. Collectively, this work uncovers a novel HDAC7/c-Myc/XPO1 signaling axis that promotes SCLC progression, suggesting that HDAC7 may warrant further investigation as a potential biomarker for assessing selinexor sensitivity in SCLC patients.
An oncolytic virus-T cell chimera for cancer immunotherapy
Chen, Yuxuan, et al. | Nature Biotechnology (2024)
Abstract:
The efficacy of oncolytic adenoviruses (OAs) for cancer therapy has been limited by insufficient delivery to tumors after systemic injection and the propensity of OAs to induce the expression of immune checkpoints. To address these limitations, we use T cells to deliver OAs into tumors and engineer the OA to express a Cas9 system targeting the PDL1 gene encoding the immune checkpoint protein PD-L1. By cloaking OAs with cell membranes presenting T cell-specific antigens, we physically conjugated OAs onto T cell surfaces by antigen-receptor interaction. We tested the oncolytic virus-T cell chimera (ONCOTECH) via intravenous delivery in mouse cancer models, including models of melanoma, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, lung cancer and glioblastoma. In the melanoma model, the in vivo delivery of ONCOTECH resulted in a strong accumulation of OAs in tumor cells, where PD-L1 expression was reduced by 50% and the single administration of ONCOTECH enabled 80% survival over 70 days. Collectively, ONCOTECH represents a promising translational technology to combine virotherapy and cell therapy.
SMAD4 endows TGF-β1-induced highly invasive tumor cells with ferroptosis vulnerability in pancreatic cancer
Hai-di Chen, et al. | Acta Pharmacol Sin (2024)
Abstract:
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is an extremely aggressive malignancy prone to recurrence and metastasis. Studies show that tumor cells with increased invasive and metastatic potential are more likely to undergo ferroptosis. SMAD4 is a critical molecule in the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) pathway, which affects the TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) status. SMAD4 loss is observed in more than half of patients with PDAC. In this study, we investigated whether SMAD4-positive PDAC cells were prone to ferroptosis because of their high invasiveness. We showed that SMAD4 status almost determined the orientation of transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1)-induced EMT via the SMAD4-dependent canonical pathway in PDAC, which altered ferroptosis vulnerability. We identified glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), which inhibited ferroptosis, as a SMAD4 down-regulated gene by RNA sequencing. We found that SMAD4 bound to the promoter of GPX4 and decreased GPX4 transcription in PDAC. Furthermore, TGF-β1-induced high invasiveness enhanced sensitivity of SMAD4-positive organoids and pancreas xenograft models to the ferroptosis inducer RAS-selective lethal 3 (RSL3). Moreover, SMAD4 enhanced the cytotoxic effect of gemcitabine combined with RSL3 in highly invasive PDAC cells. This study provides new ideas for the treatment of PDAC, especially SMAD4-positive PDAC.
An RNA helicase DHX33inhibitor shows broad anticancer activity via inducing ferroptosis in cancer cells
Xiyu Tang, et al. | ACS OMEGA (2024)
Abstract:
RNA helicase DHX33 has been identified as a critical factor promoting cancer development. In the present study, a previously developed small molecule inhibitor for DHX33, KY386, was found to robustly kill cancer cells via a new path, the ferroptosis pathway. Mechanistically, DHX33 promotes the expression of critical players in lipid metabolism including FADS1, FADS2, and SCD1 genes, thereby sensitizing cancer cells to ferroptosis mediated cell death. Our study reveals a novel mechanism of DHX33 in promoting tumorigenesis and highlights that pharmacological targeting DHX33 can be a feasible option in human cancers. Normally differentiated cells are insensitive to DHX33 inhibition, and DHX33 inhibitors have little cellular toxicity in vitro and in vivo. Our studies demonstrated that DHX33 inhibitors can be promising anticancer agents with great potential for cancer treatment.
暂无文献引用
COA查询
根据货号和批次号,在线查询已购买产品的COA证书
请输入产品货号(REF or CAT Number) 和产品批号(LOT Number) ,查询COA证书文件。
产品货号和产品批号均显示在产品标签上对应位置(如右侧示意图所示)
产品货号和产品批号均显示在产品标签上对应位置(如右侧示意图所示)
产品货号
﹡
产品批号
﹡
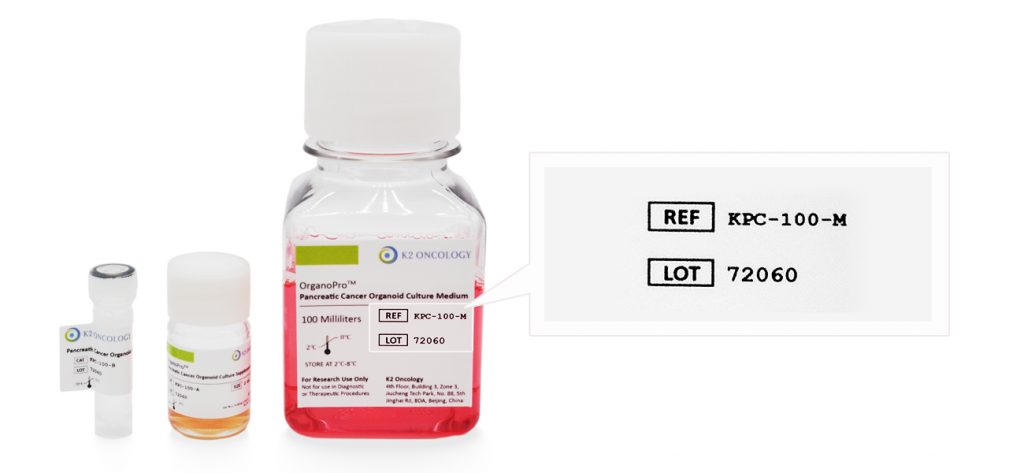
Ref/Cat#
产品货号,每个产品对应的独立货号
Lot#
批次编号,同一产品不同批次会有不同批号,请您在产品包装找到对应批号