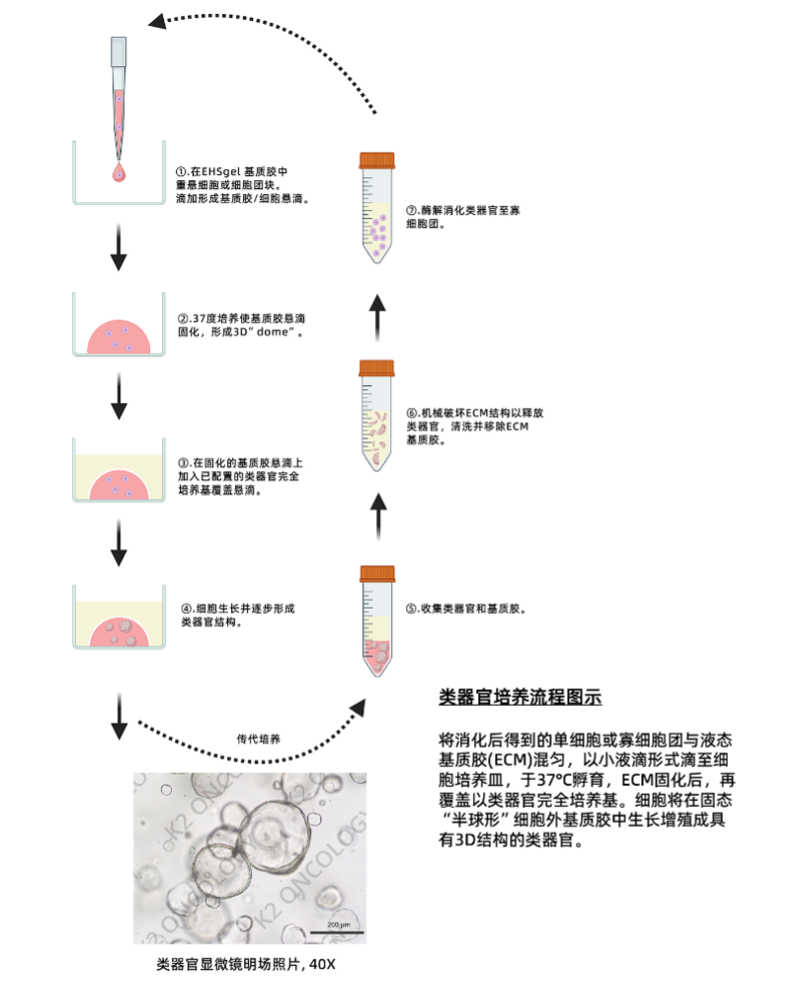
-
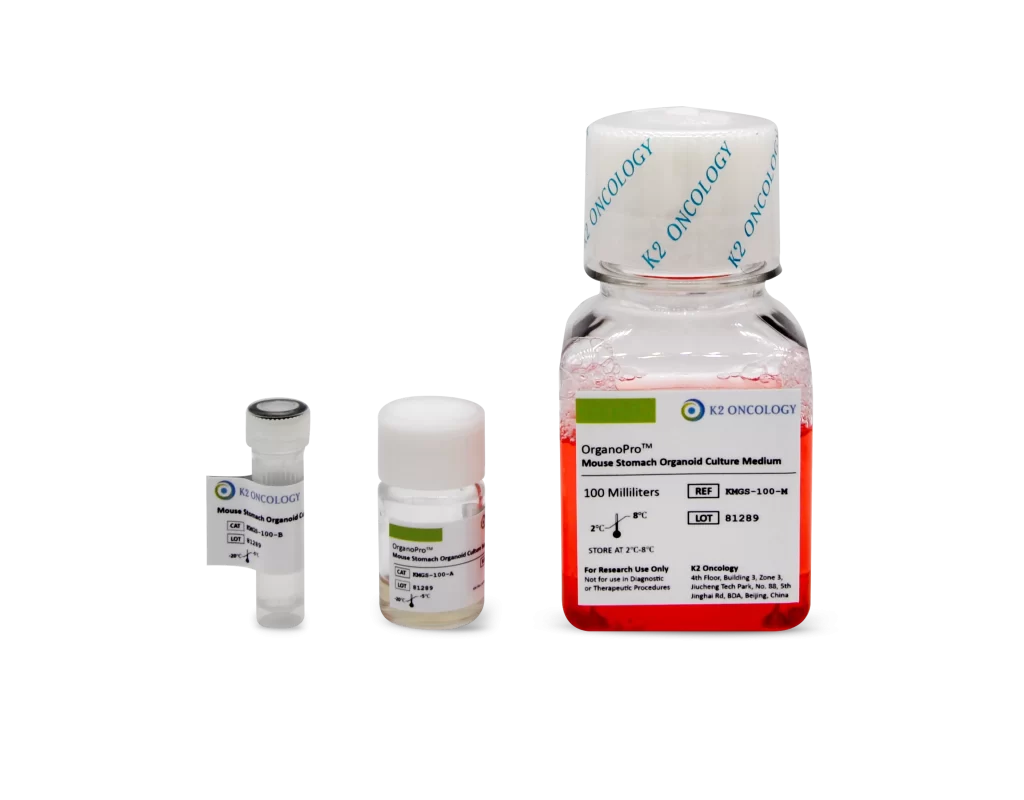
小鼠胃组织类器官培养试剂盒
KMGS-100
-
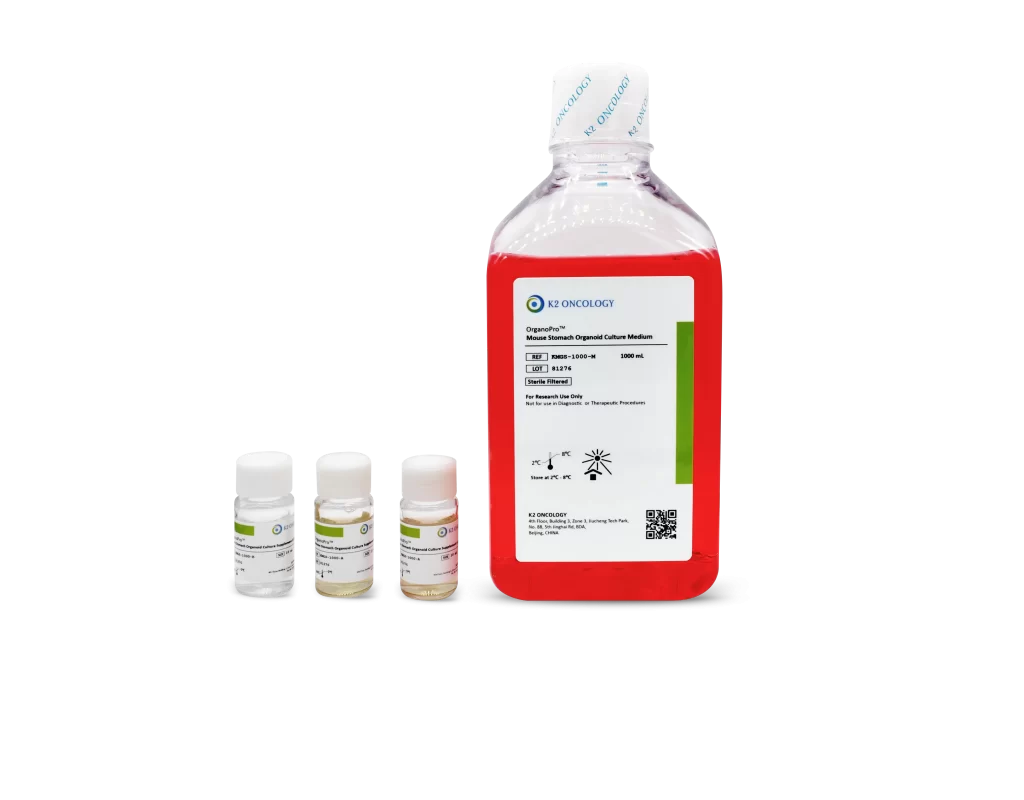

小鼠胃组织类器官培养试剂盒
KMGS-1000

OrganoPro™小鼠胃组织类器官培养基套装
KMGS-100 包含以下产品
- OrganoPro™小鼠胃组织培养基 100mL
- OrganoPro™小鼠胃组织添加剂成分A 2mL
- OrganoPro™小鼠胃组织添加剂成分B 1mL
KMGS-1000 包含以下产品
- OrganoPro™小鼠胃组织培养基 1000mL
- OrganoPro™小鼠胃组织添加剂成分A 10mL x 2
- OrganoPro™小鼠胃组织添加剂成分B 10mL
科途医学 科学家

名字
PhD
我们的科学家向您推荐
我们的产品简化了实验流程,集成多种因子,无需单独优化,扩增潜力高,14天内细胞数量可达到1×10^6。适用于多种培养形式,包括基质胶、低吸附孔板和生物反应器悬浮培养。GMP级别生产条件下制备,批次质量稳定,试剂含量是常规市售干细胞培养基的2倍,实现极佳的成本效益比。让复杂的培养变得简单快速,让科研变得更高效。
概览
产品组成:
| 产品名称 | 货号 | 规格 | 储存温度 | 保质期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OrganoPro™ Mice Gastric Organoid Culture Medium 小鼠胃组织类器官培养基 | KMGS-100/1000-M | 100mL / 1000mL | 2-8°C | 12个月 |
| OrganoPro™ Mice Gastric Organoid Culture Supplement A(50X) 小鼠胃组织类器官培养基添加剂A(50X) | KMGS-100/1000-A | 2mL / 20mL | -20°C | 12个月 |
| OrganoPro™ Mice Gastric Organoid Culture Supplement B(100X) 小鼠胃组织类器官培养基添加剂B(100X) | KMGS-100/1000-B | 1mL / 10mL | -20°C | 12个月 |
类型
类器官培养基
适用细胞
小鼠胃组织
物种
小鼠
应用
培养小鼠胃组织类器官
商标
OrganoPro™
产品使用说明及支持信息
在产品文档中查找支持信息和使用说明,或在下方探索更多
| 文档类型 | 产品名称 | Catalog # |
|---|---|---|
| User manual | OrganoPro™ 小鼠胃组织类器官培养基套装 | KMGS-100 KMGS-1000 |
资源及文献引用
相关资源及文献引用
preclinical evaluation of CAR-T cell immunotherapy with a fully human EpCAM-specific sdFv against pancreatic cancer
Ying-Ying Fan, et al. | Cancer Immunol immunother. 2025 Dec 19; 75(1):22.
ABSTRACT:
Pancreatic cancer is an aggressive malignancy with poor prognosis. Recent advances in chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell immunotherapy have offered renewed hope. The pivotal factors determining the effectiveness of CAR-T cells in the clinic is the selection of a reliable target and a specific ectodomain of CAR molecule. EpCAM is widely expressed in epithelial tumors, including pancreatic cancer, and is used as a tumor target in clinical trials of CAR-T cell therapy for gastric and colorectal cancers. However, the feasibility of using EpCAM CAR-T cells in pancreatic cancer still needs to be verified. In this work, we reported novel EpCAM CAR-T cells with a fully human single-chain variable fragment and evaluated their cytotoxic effects in a panel of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell lines, three-dimensional tumor spheroid models and patient-derived organoids, and two xenograft mouse models. We demonstrated that EpCAM CAR-T cells exhibited potent and specific anti-tumor activity against EpCAM positive pancreatic cancer in vitro and in vivo, without adverse effects by systematic delivery in xenograft mouse models. Our preclinical results provided evidence of the efficacy and feasibility of EpCAM CAR-T cells for the immunotherapy of pancreatic cancer.
Lipidomics and single‐cell transcriptomics uncover aberrant lipid metabolism in metaplasia lesions during gastric carcinogenesis
Huan Wang, et al. | J Gastroenterol. 2025 Nov 14.
ABSTRACT:
Background: Gastric intestinal metaplasia (GIM) is a precancerous lesion that elevates gastric cancer risk. Our prior single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis implied aberrant lipid metabolism in GIM. We also established a Ddit4-deficient mouse model that developed severe gastric metaplasia lesions upon Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection. This study aims to define the lipid signatures of metaplasia lesions in gastric carcinogenesis.
Methods: We performed lipidomic analysis of gastric tissues from H. pylori-infected Ddit4-/- and wild-type (WT) mice, and from human GIM and chronic non-atrophic gastritis (CNAG) samples. scRNA-seq data were reanalyzed to identify lipid metabolism-related gene expression during GIM progression. The therapeutic effects of lipid inhibitors sulfosuccinimidyl oleate sodium (SO), TVB3664 and fenofibrate, were evaluated in patient-derived gastric cancer organoids and in a tamoxifen (TAM)-induced gastric metaplasia mouse model. Immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and BODIPY 505/515 staining were also conducted.
Results: Lipidomic profiling revealed a marked increase in triglyceride (TG) levels in Ddit4-/- mice with gastric metaplasia. Similarly, human GIM tissues showed elevated TG content compared to CNAG. BODIPY staining confirmed lipid droplet (LD) accumulation in GIM. GSEA analysis of scRNA-seq data indicated upregulation of TG metabolism and synthesis pathways in GIM. Key genes involved in TG synthesis (DGAT1, MOGAT2, MOGAT3) and fatty acid (FA) transport (FABP1, FABP2, SLC27A4) were significantly elevated in GIM. Notably, DGAT1 protein levels were substantially upregulated in human GIM tissues relative to CNAG controls. In contrast, certain membrane lipids like lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) subclasses were reduced in GIM. FA transport inhibitor SO and synthesis inhibitor TVB3664 suppressed gastric cancer organoid growth. In mice, TVB3664 and fenofibrate alleviated gastric pathology including inflammation and metaplasia.
Conclusions: Our study reveals a distinct lipid signature in gastric metaplasia characterized by TG and LD accumulation, providing novel therapeutic insights into targeting lipid metabolism to prevent GIM malignant transformation and reduce cancer risk.
Discovery of C19-9 as a novel non-RGD inhibitor of αvβ3 to overcome enzalutamide resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer
Pang, X., Sun, X., Gu, Y. et al. | Sig Transduct Target Ther (2023)
Abstract:
The integrin αvβ3 receptor is a promising target for anticancer therapy.1,2 However, there are no effective marketed treatments targeting αvβ3. One possible limitation of Arginine-Glycine-Aspartic (RGD)-mimetic αvβ3 antagonists has been shown to cause partial agonism, which could induce major conformational changes that trigger paradoxical cell adhesion and angiogenesis.
Read More: https://doi.org/10.1038%2Fs41392-022-01236-z 暂无文献引用
COA查询
根据货号和批次号,在线查询已购买产品的COA证书
请输入产品货号(REF or CAT Number) 和产品批号(LOT Number) ,查询COA证书文件。
产品货号和产品批号均显示在产品标签上对应位置(如右侧示意图所示)
产品货号和产品批号均显示在产品标签上对应位置(如右侧示意图所示)
产品货号
﹡
产品批号
﹡
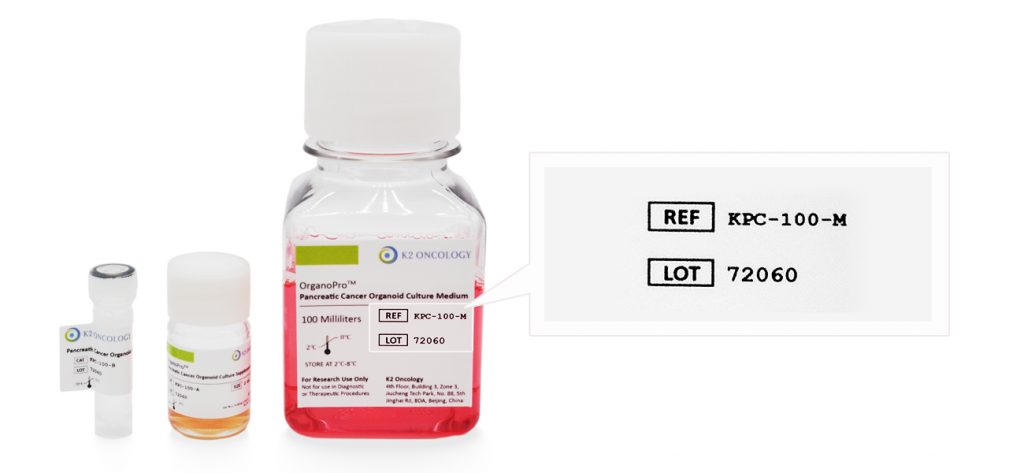
Ref/Cat#
产品货号,每个产品对应的独立货号
Lot#
批次编号,同一产品不同批次会有不同批号,请您在产品包装找到对应批号