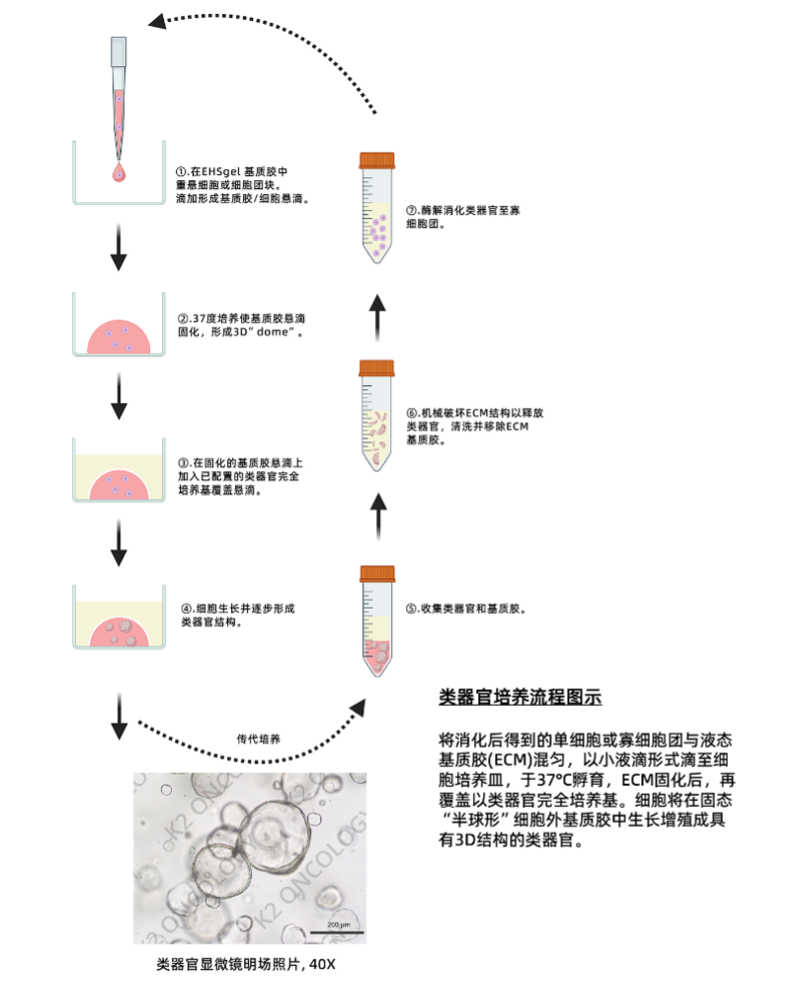
-
肝癌类器官培养试剂盒
KLV-100
-

肝癌类器官培养试剂盒
KLV-1000


OrganoPro™肝癌类器官培养基套装
KLV-100 包含以下产品
- OrganoPro™肝癌培养基 100mL
- OrganoPro™肝癌添加剂成分A 2mL
- OrganoPro™肝癌添加剂成分B 1mL
KLV-1000 包含以下产品
- OrganoPro™肝癌培养基 1000mL
- OrganoPro™肝癌添加剂成分A 10mL x 2
- OrganoPro™肝癌添加剂成分B 10mL

我们的科学家向您推荐
我们的产品简化了实验流程,集成多种因子,无需单独优化,扩增潜力高,14天内细胞数量可达到1×10^6。适用于多种培养形式,包括基质胶、低吸附孔板和生物反应器悬浮培养。GMP级别生产条件下制备,批次质量稳定,试剂含量是常规市售干细胞培养基的2倍,实现极佳的成本效益比。让复杂的培养变得简单快速,让科研变得更高效。
概览
此产品基于 Simumatrix 技术平台,通过工业化高通量筛选,针对中国高发的肿瘤类型进行培养基优化筛选而开发出的类器官培养基产品,可用于肝癌的类器官培养。
产品优势/特点:
- 简单易用,节省验证时间:提供详细操作方案,产品使用简便,节省研究者大量类器官培养摸索验证时间;
- 肿瘤组织覆盖类型广:覆盖多达15个组织瘤种,>900种肿瘤驱动基因突变模型;
- 扩增潜力高:自研高活力高稳定性WNT与RSPOs,支持肿瘤类器官多代次连续稳定培养;
- 肿瘤类器官验证数据齐备:多维类器官验证数据的整合,类器官驱动基因突变及表达谱,类器官组织病理学验证及类器官药敏数据等。
- 多篇高分文献应用:多篇高分文献应用,口碑卓越;
- 自主研发,产能充足,性价比高:全自研生产,源头品控,产品性价比高。
产品组成:
| 产品名称 | 货号 | 规格 | 储存温度 | 保质期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OrganoPro™ Liver Cancer Organoid Culture Medium 人源肝癌类器官培养基 | KLV-100/1000-M | 100mL / 1000mL | 2-8°C | 12个月 |
| OrganoPro™Liver Cancer Organoid Culture Supplement A(50X) 人源肝癌类器官培养基添加剂A(50X) | KLV-100/1000-A | 2mL / 20mL | -20°C | 12个月 |
| OrganoPro™ Liver Cancer Organoid Culture Supplement B(100X) 人源肝癌类器官培养基添加剂B(100X) | KLV-100/1000-B | 1mL / 10mL | -20°C | 12个月 |
类型
类器官培养基
适用细胞
肝癌类器官
物种
人类
应用
培养人源肝癌类器官
商标
OrganoPro™
产品使用说明及支持信息
在产品文档中查找支持信息和使用说明,或在下方探索更多
| 文档类型 | 产品名称 | Catalog # |
|---|---|---|
| User manual | OrganoPro™ 肝癌类器官培养基套装 | KLV-100 KLV-1000 |
资源及文献引用
相关资源及文献引用
Cationic alkyl chain length and nanoaggregate form of ionic liquids dominate biocompatibility and toxicity
Yuyuan Xing, et al. | Nat Commun. (2025) Jul 28;16 (1): 6929.
ABSTRACT:
Integrative multiomics analysis identifies molecular subtypes and potential targets of hepatocellular carcinoma
Shuai Yang, et al. | Clin Transl Med (2024)
Abstract:
Background: The liver is anatomically divided into eight segments based on the distribution of Glisson's triad. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying each segment and its association with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) heterogeneity are not well understood. In this study, our objective is to conduct a comprehensive multiomics profiling of the segmentation atlas in order to investigate potential subtypes and therapeutic approaches for HCC.
Methods: A high throughput liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometer strategy was employed to comprehensively analyse proteome, lipidome and metabolome data, with a focus on segment-resolved multiomics profiling. To classify HCC subtypes, the obtained data with normal reference profiling were integrated. Additionally, potential therapeutic targets for HCC were identified using immunohistochemistry assays. The effectiveness of these targets were further validated through patient-derived organoid (PDO) assays.
Results: A multiomics profiling of 8536 high-confidence proteins, 1029 polar metabolites and 3381 nonredundant lipids was performed to analyse the segmentation atlas of HCC. The analysis of the data revealed that in normal adjacent tissues, the left lobe was primarily involved in energy metabolism, while the right lobe was associated with small molecule metabolism. Based on the normal reference atlas, HCC patients with segment-resolved classification were divided into three subtypes. The C1 subtype showed enrichment in ribosome biogenesis, the C2 subtype exhibited an intermediate phenotype, while the C3 subtype was closely associated with neutrophil degranulation. Furthermore, using the PDO assay, exportin 1 (XPO1) and 5-lipoxygenase (ALOX5) were identified as potential targets for the C1 and C3 subtypes, respectively.
Conclusion: Our extensive analysis of the segmentation atlas in multiomics profiling defines molecular subtypes of HCC and uncovers potential therapeutic strategies that have the potential to enhance the prognosis of HCC.
GSTA1/CTNNB1 axis facilitates sorafenib resistance via suppressing ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
Shiwen Ma, et al. | Pharmacol Res (2024)
Abstract:
暂无文献引用
COA查询
根据货号和批次号,在线查询已购买产品的COA证书
产品货号和产品批号均显示在产品标签上对应位置(如右侧示意图所示)
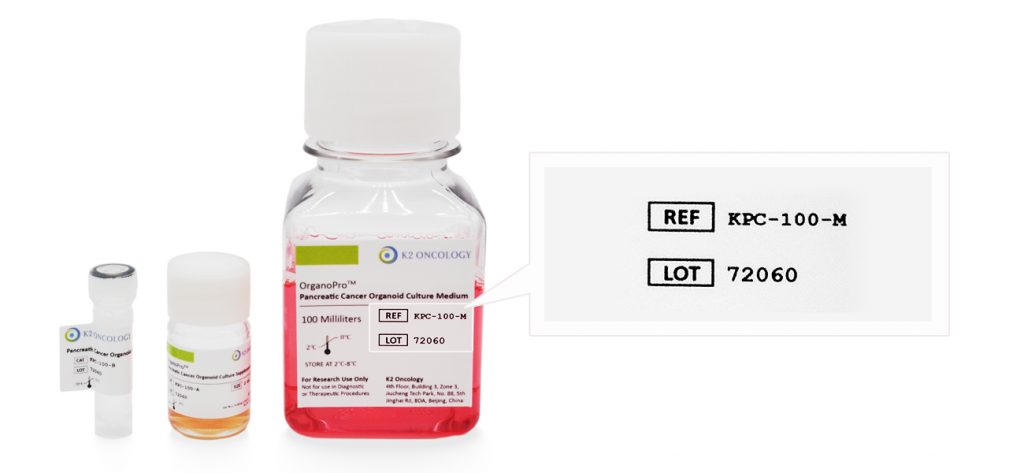
Ref/Cat#
产品货号,每个产品对应的独立货号
Lot#
批次编号,同一产品不同批次会有不同批号,请您在产品包装找到对应批号