Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer KRAS G12D Mutant Organoids
1. PRODUCT INFORMATION
Patient derived tumor organoids (PDOs) have emerged as powerful pre-clinical models, which can closely recapitulate of the genetic and morphological characteristics of the original tumor. PDOs models are used to facilitate drug discovery and translational medicine studies.
2.CELL CHARACTERISTICS
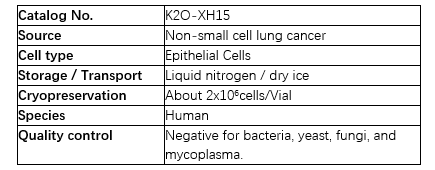
2.1 Bright field images of the K2O-XH15 organoids
K2O-XH15 organoids were cultured in Matrigel for one week. Afterward, the morphology were observed and photographed with an inverted phase contrast microscope (Fig.1).
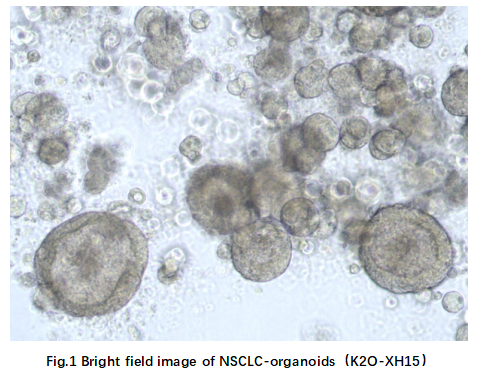
2.2 Proliferation characteristics
The proliferation characteristics of organoids were visaliized with a proliferation curve by determining the cell viability daily with a CellTiter-Glo® 3D cell viability assay (Fig.2).
3. GENETIC MUTATION
3.1 Sanger sequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted from PDO cell pellets and was amplified by PCR at KRAS exon 2, 3 and 4. Sanger sequencing shows a mutant-only peak at position 35 consistent with a G12D mutation (35G>A) Thus, it could be concluded that KRASG12D mutation occurred in K2O-XH15(Fig.3). Sequencing electropherogram of KRASG12D mutation are shown in Figure 3.
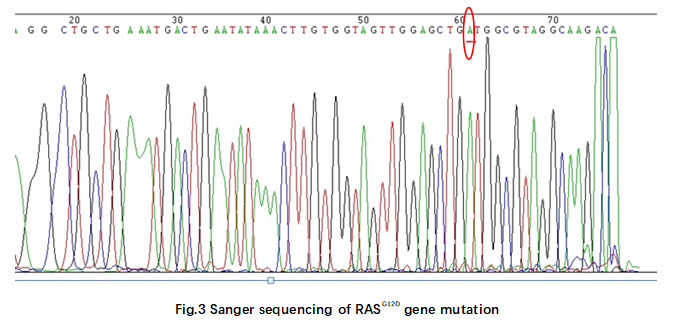
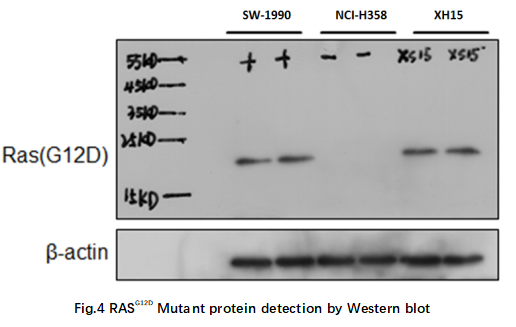
3.2 KRAS G12D mutation in protein level
Pellets of KRAS G12D mutant cell line SW-1990 , KRAS G12C cell line NCI-H358 and K2O-XH15 organoids were collected. Lysates were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with anti-RAS G12D specific antibody. Positive signals of SW-1990 and K2O-XH15 were observed at 21kDa, while KRAS G12C mutant NCI-H358 cells cannot be detected. Therefore, K2O-XH15 organoids express KRAS G12D mutant protein (Fig.4).
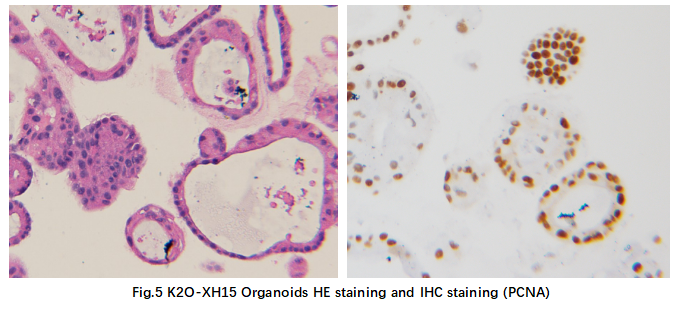
4.HISTOPATHOLOGICAL FEATURE
HE staining and IHC staining were conducted to evaluate the organoids histopathological structure. K2O-XH15 organoids retain the lung cancer tissue characteristics.
5.PHARMACOLOGICAL FEATURE
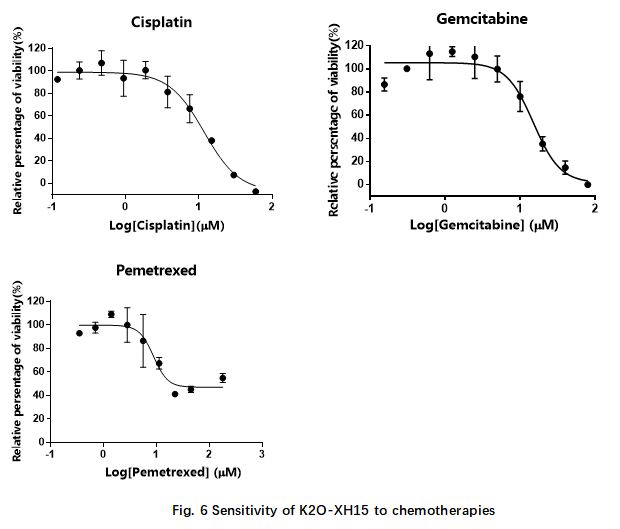
5.1 Standard chemotherapies
To evaluate the in vitro sensitivity of K2O-XH15 to 1st line chemotherapies, cell viabiltiy assay were conducted to test the sensitivity of K2O-XH15 to Cisplatin, Gemcitabine and Pemetrexed in Fig. 6.
5.2 Target drug efficacy test
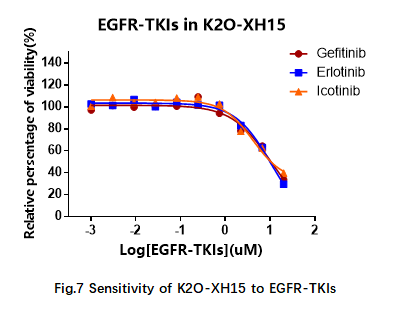
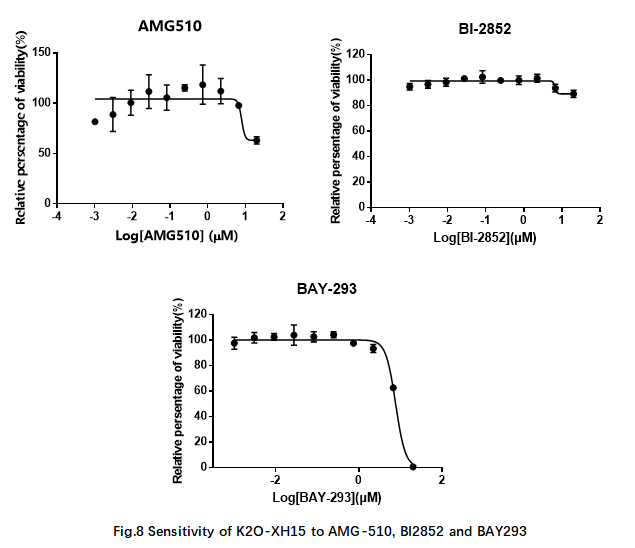
There are many types of targeted drugs depending on the mutations carried by NSCLC patients. Among them, EGFR-TKIs is the most common targeted drug. In addition, RAS small molecule drug candidates in clinical development stage were tested. In this test, it can be determined that RAS G12D mutant organoids are not sensitive to EGFR-TKIs (Fig.7) BI2852 and BAY293 and AMG510 (Fig.8).
6.PDOX MOUSE MODEL
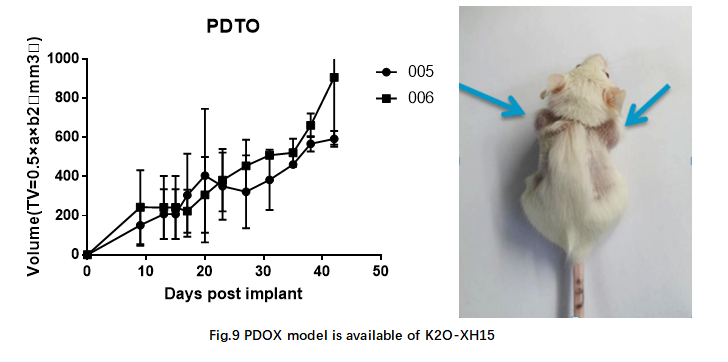
Patient derived tumor organoids were expanded in vitro and implanted into NOG mice subcutaneously. Tumor volume is measured and photographed regularly. K2O-XH15 NSCLC-organoids can rapidly form xenograft in immunodeficiency mice (Fig. 9).
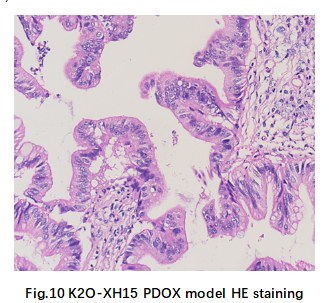
Tumor tissues were harvested from PDOX after sacrificed. Histopathological staining showed typical lung cancer adenocarcinoma phenotype (Fig. 10).
7. BACKGROUND
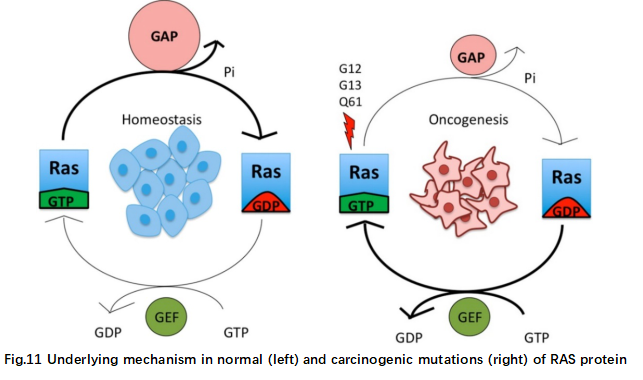
RAS proteins are GTPases (small G proteins). The on / off state of the RAS protein is determined by nucleotide binding. When GTP binds to RAS, RAS is activated, and when GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP, RAS is inactivated.
RAS mutant is an oncogene, accounting for an average of 25% of human cancers, the highest of all oncogene mutations. One million people worldwide die from cancer each year due to KRAS mutations. The missense mutation in the mutant protein changes the steady state balance of GDP and GTP by reducing GTP hydrolysis (G12, Q61), or by increasing the GTP loading rate (G13, K117), or nucleotide exchange (A146), thereby continuously activating the signaling pathway (Fig. 11).
Organoid model is a three-dimensional cell culture system which is highly similar to the source tissue or organ in vivo. These 3D systems can well recapitulate the complex spatial morphology of differentiated tissues and can show cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions. Organoid models are being used more and more in preclinical research and development of new drugs (Fig.12).