-
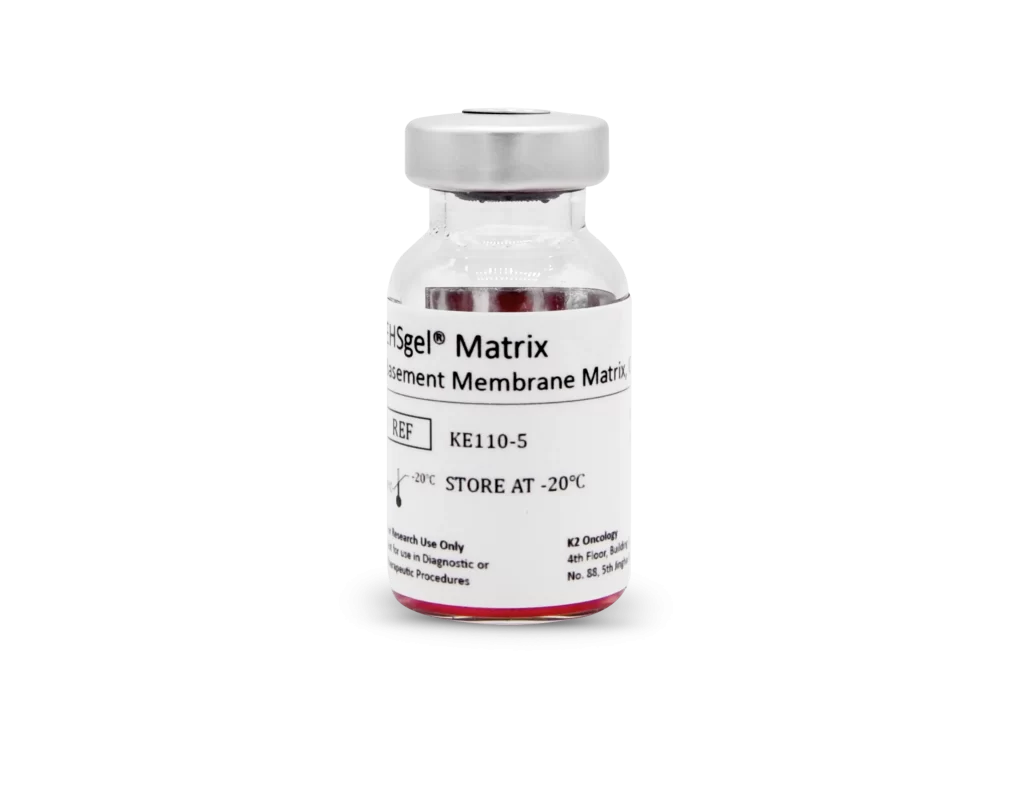
EHSgel® 低生长因子型基质胶
KE110-5
-

EHSgel® 低生长因子型基质胶
KE110-10

EHSgel® 低生长因子型基质胶
EHSgel® matrix基质胶为细胞培养提供更加接近生理条件的微环境,适用于类器官培养、干细胞维持和分化,血管生成,肿瘤浸润,体内疾病模型构建及再生医学等多种实验或研究领域。
Catalog #KE110-5 #KE110-10
低生长因子型基质胶,类器官培养,3D 微球培养,血管生成研究,干细胞培养和分化及其它对生长因子背景信号敏感的相关研究中使用
KE110-5 包含以下产品
- EHSgel® 低生长因子型基质胶 5mL
KE110-10 包含以下产品
- EHSgel® 低生长因子型基质胶 10mL

我们的科学家向您推荐
我们的产品简化了实验流程,集成多种因子,无需单独优化,扩增潜力高,14天内细胞数量可达到1×10^6。适用于多种培养形式,包括基质胶、低吸附孔板和生物反应器悬浮培养。GMP级别生产条件下制备,批次质量稳定,试剂含量是常规市售干细胞培养基的2倍,实现极佳的成本效益比。让复杂的培养变得简单快速,让科研变得更高效。
概览
产品特点:
- 从富含细胞外基质蛋白的小鼠Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm (EHS)肉瘤中提取纯化制备
- 主要成分:
- 层粘连蛋白(Laminin)
- IV型胶原蛋白(Collagen IV)
- 粘连蛋白/重复序列蛋白(Entactin/Nidogen)
- 硫酸乙酰肝素蛋白多糖(Heparin sulfate proteoglycan)
- 多种细胞因子,如TGF-β1、IGF、FGF等(Growth Factor Reduced版本已去除这些小分子蛋白)
- 在37°C下自组装成超级分子结构,在物理特性、组成成分和功能特征方面与天然基底膜类似
- 为细胞培养提供更加接近生理条件的微环境
- 适用于:
- 类器官培养
- 干细胞维持和分化
- 血管生成
- 肿瘤侵袭
- 体内疾病模型构建
- 再生医学等多种实验或研究领域
- 通过ELISA定量检测,证实EHSgel含有显著高于竞品MG的4种主要基底膜基质蛋白
- 经过严格的质量控制测试,包括蛋白浓度、主要成分含量、MMP2残留、蛋白电泳、成胶性、稳定性、支持多种类器官培养的能力、血管生成、体内成瘤性、内毒素水平、无菌性和鼠源病毒安全性等
- 在人非小细胞肺癌、乳腺癌、卵巢癌、胃癌和胆管癌样本的类器官培养中表现出优于竞品MG的性能
- 能够促进人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVEC)的体外血管生成,与竞品MG相当
- 在移植瘤模型中,显著增强MDA-MB-231三阴性乳腺癌细胞系的体内成瘤率和生长速度,与MG相媲美
- 提供标准型和低生长因子型两种规格,可选择含酚红或无酚红版本
| 产品名称 | 货号 | 规格 | 储存温度 | 保质期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EHSgel® Basement Membrane Matrix GFR EHSgel® 低生长因子型基质胶 | KE110-5/10 | 5mL / 10mL | -20°C | 12个月 |
类型
基质胶
适用细胞
类器官/细胞
物种
人类
应用
类器官培养/3D微球培养/体内成瘤实验
商标
EHSgel®
产品使用说明及支持信息
在产品文档中查找支持信息和使用说明,或在下方探索更多
| 文档类型 | 产品名称 | Catalog # |
|---|---|---|
| User manual | EHSgel® 低生长因子型基质胶 | KE110-5 KE110-10 |
资源及文献引用
相关资源及文献引用
Organoid drug screening report for a non-small cell lung cancer patient with EGFR gene mutation negativity: A case report and review of the literature
Pan, Yuetian, Hongshang Cui, and Yongbin Song | Frontiers in Oncology (2023)
Abstract:
Identification of solamargine as a cisplatin sensitizer through phenotypical screening in cisplatin-resistant NSCLC organoids
Han, Yi,et al. | Frontiers in Pharmacology (2022)
Abstract:
An Artemisinin Derivative ART1 Induces Ferroptosis by Targeting the HSD17B4 Protein Essential for Lipid Metabolism and Directly Inducing Lipid Peroxidation.
Xie, Jingjing, et al. | CCS Chemistry (2022)
Abstract:
Artemisinin and its derivatives, commonly known as antimalarial drugs, have gradually come to be regarded as potential antitumor agents, although their cytotoxic efficacy and mechanisms of action remain to be settled. Herein, we report that an artemisinin analog, ART1, can potently induce ferroptosis in a subset of cancer cell lines. Structure–activity relationship (SAR) analysis reveals that both the endoperoxide moiety and the artemisinin skeleton are required for the antitumor activity of ART1. Aided with ART1-based small-molecule tools, chemical proteomic analysis identified the HSD17B4 protein as a direct target of ART1. HSD17B4 resides in peroxisomes and is an essential enzyme in the catabolism of very-long-chain fatty acids. Our results demonstrate that ART1 initiates ferroptosis through selective oxidation of the fatty acids in peroxisomes by hijacking the HSD17B4 protein without disturbing its enzymatic function, providing a promising mechanism to develop therapeutics for cancer treatment. Read More: https://doi.org/10.31635/ccschem.021.202000691Pyrotinib in patients with HER2-amplified advanced non–small cell lung cancer: A prospective, multicenter, single-arm trial
Song, Zhengbo,et al. | Clinical Cancer Research (2022)
Abstract:
Glutamine synthetase licenses APC/C-mediated mitotic progression to drive cell growth
Zhao, Jiang-Sha,et al. | Nature Metabolism (2022)
Abstract:
Halofuginone sensitizes lung cancer organoids to cisplatin via suppressing PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways
Li, Hefei,et al. | Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology (2021)
Abstract:
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Cisplatin is the major DNA-damaging anticancer drug that cross-links the DNA in cancer cells, but many patients inevitably develop resistance with treatment. Identification of a cisplatin sensitizer might postpone or even reverse the development of cisplatin resistance. Halofuginone (HF), a natural small molecule isolated from Dichroa febrifuga, has been found to play an antitumor role. In this study, we found that HF inhibited the proliferation, induced G0/G1 phase arrest, and promoted apoptosis in lung cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner. To explore the underlying mechanism of this antitumor effect of halofuginone, we performed RNA sequencing to profile transcriptomes of NSCLC cells treated with or without halofuginone. Gene expression profiling and KEGG analysis indicated that PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways were top-ranked pathways affected by halofuginone. Moreover, combination of cisplatin and HF revealed that HF could sensitize the cisplatin-resistant patient-derived lung cancer organoids and lung cancer cells to cisplatin treatment. Taken together, this study identified HF as a cisplatin sensitizer and a dual pathway inhibitor, which might provide a new strategy to improve prognosis of patients with cisplatin-resistant lung cancer.
COA查询
根据货号和批次号,在线查询已购买产品的COA证书
产品货号和产品批号均显示在产品标签上对应位置(如右侧示意图所示)
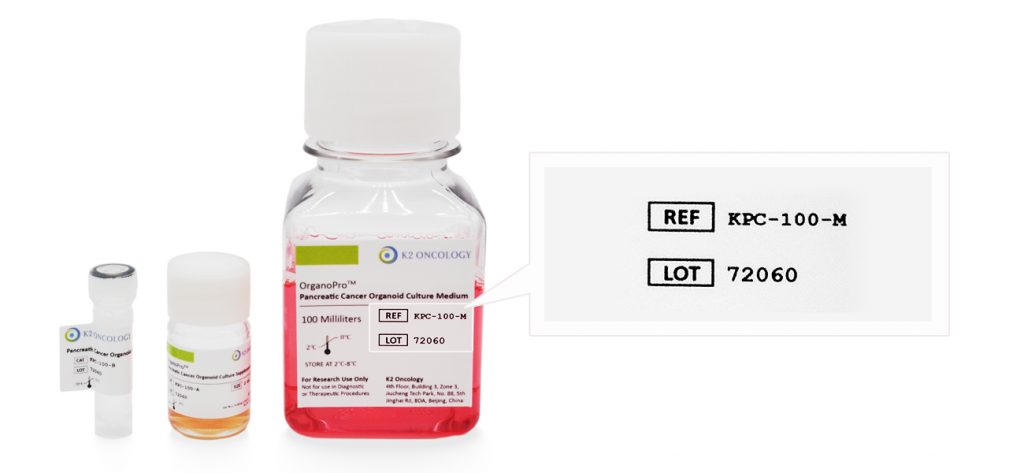
Ref/Cat#
产品货号,每个产品对应的独立货号
Lot#
批次编号,同一产品不同批次会有不同批号,请您在产品包装找到对应批号



